
Background: After seven decades as a constituent republic of the USSR, Belarus attained its independence in 1991. It has retained closer political and economic ties to Russia than any of the other former Soviet republics. Belarus and Russia signed a treaty on a two-state union on 8 December 1999 envisioning greater political and economic integration but, to date, neither side has actively sought to implement the accord.
Geography
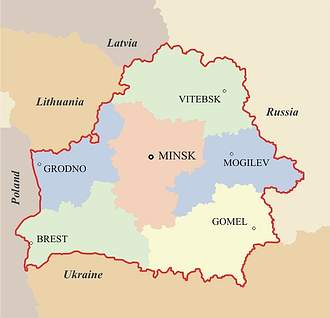
Location: Eastern Europe, east of Poland
Geographic coordinates: 53 00 N, 28 00 E
Map references: Commonwealth of Independent States
Songs of
the famour Belarusian folk group PESNYARY (MP3)
 Area:
Area:
total: 207,600 sq km
land: 207,600 sq km
water: 0 sq km
Area - comparative: slightly smaller than Kansas
Land boundaries:
total: 3,098 km
border countries: Latvia 141 km, Lithuania 502
km, Poland 605 km, Russia 959 km, Ukraine 891 km
Coastline: 0 km (landlocked)
Maritime claims: none (landlocked)
Climate: cold winters, cool and moist summers; transitional between continental and maritime
Terrain: generally flat and contains much marshland

Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Nyoman River 90 m
highest point: Dzyarzhynskaya Hara 346 m
Natural resources: forests, peat deposits, small quantities of oil and natural gas
Land use:
arable land: 29%
permanent crops: 1%
permanent pastures: 15%
forests and woodland: 34%
other: 21% (1993 est.)
Irrigated land: 1,000 sq km (1993 est.)

Natural hazards: NA
Environment - current issues: soil pollution from pesticide use; southern part of the country contaminated with fallout from 1986 nuclear reactor accident at Chornobyl' in northern Ukraine
Environment - international agreements:
party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen
Oxides, Air Pollution-Sulphur 85, Biodiversity, Endangered Species, Environmental
Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Marine Dumping, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone
Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: Climate Change, Law
of the Sea
Geography - note: landlocked
Source: The World Factbook of Central Intelligence
Agency